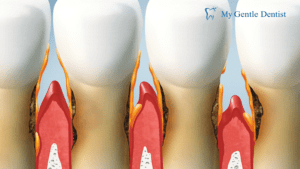
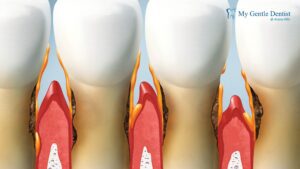
What are Gum Diseases?
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is one of the most common oral diseases. Also known as periodontitis. Is it possible for periodontal disease to cause teeth to fall out? It may sound like a simple question but the reality of periodontal disease is far more complex.
In this blog post, we explore the surprising truth about periodontal disease, the causes behind it, and the long-term implications it can have on your oral health.
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that is characterized by bleeding and inflammation of the gums. Most cases of gingivitis are reversible with proper oral health. From the possible causes to the treatments available, we uncover what you need to know about periodontal disease so you can take the necessary steps to protect your teeth.
What are signs of severe Gum Disease?

Gingivitis is the term for periodontal disease’s early stages. Although gingivitis typically does not hurt, it can nonetheless exhibit some Symptoms of Periodontal Disease, such as:
- Bleeding gums
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bad breath
- Gums that pull away from the teeth
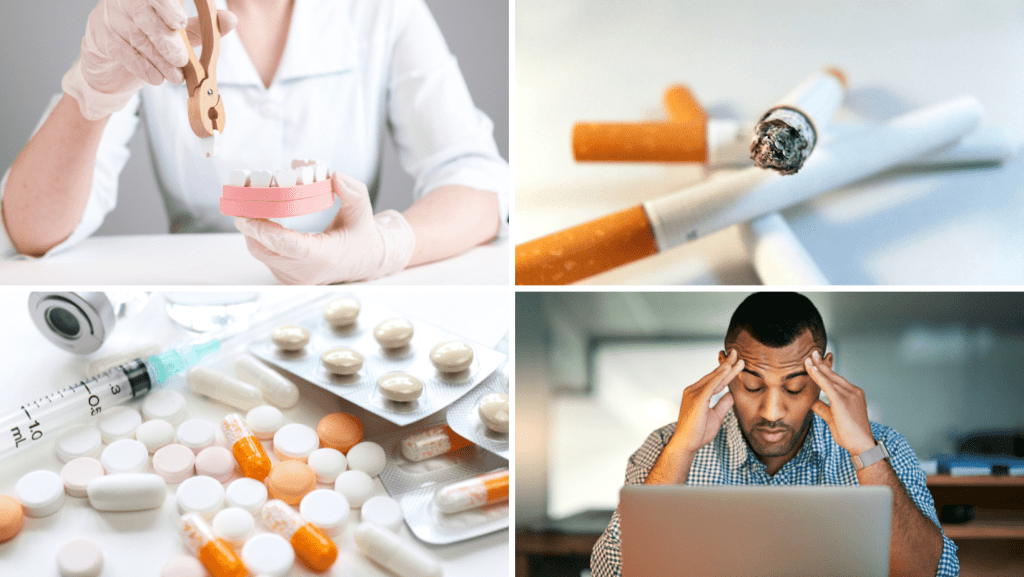
The most common cause of periodontal disease is bacteria. Bacteria, including the kinds that cause plaque, form on the teeth, gums, and tongue. These bacteria cause inflammation and infection in the gums, which then leads to the destruction of gum tissue, bone, and teeth.
There are several different causes of periodontal disease, including:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque buildup and the subsequent development of periodontal disease. Plaque is made up of bacteria and food particles that are not removed by brushing or flossing. As plaque accumulates and hardens, it becomes difficult to remove, leaving gums vulnerable to infection.
Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for periodontal disease. Smoking can interfere with the body’s ability to fight bacteria and can leave gums vulnerable to infection and the development of periodontal disease.
Certain Medications: Some medications, such as certain types of antibiotics, can affect the balance of bacteria in the mouth and increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Diseases: Diseases such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and heart disease can all contribute to periodontal disease. Diabetes and HIV/AIDS can increase the risk of infection, and heart disease can affect circulation and the body’s ability to fight infection.
Genetic Factors: Periodontal disease is more common in some families, suggesting that genetic factors can play a role in its development.
Stress: Stress can affect the body’s ability to fight infection and, as a result, can increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Poor Diet: A diet low in essential vitamins and minerals can lead to the development of periodontal disease.
How gum Disease is treated?
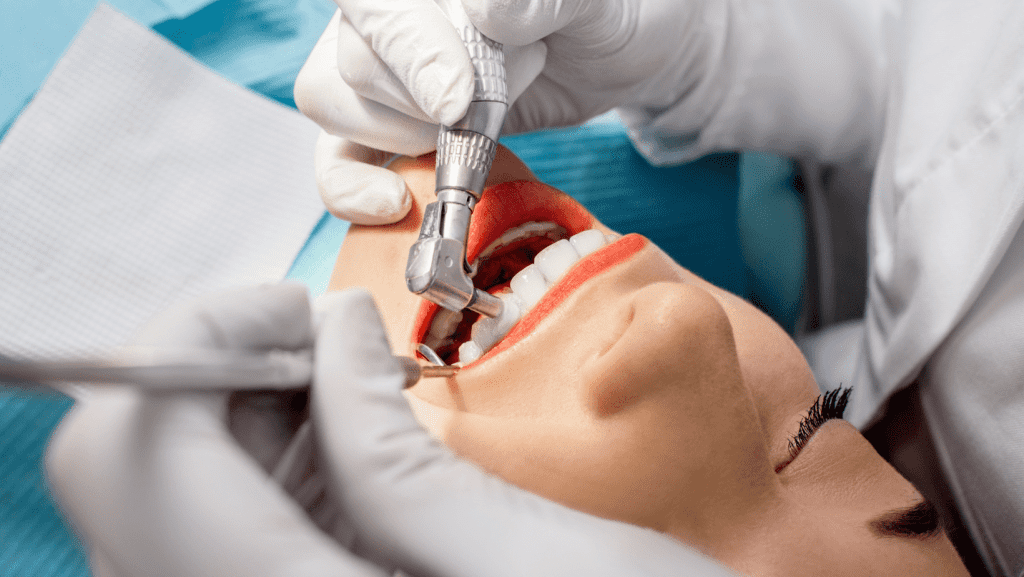
Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums and other tissues that support your teeth. When left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage and treat periodontal disease.
Professional Cleanings
Regular cleanings by a dentist or dental hygienist are an important part of maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing periodontal disease. During a cleaning, your dentist or hygienist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth, which can lead to gum disease. Your dentist or hygienist may also recommend that you use an electric toothbrush to help remove plaque.
Antibacterial Mouthwash
Using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the bacteria in your mouth, limiting the development of plaque and tartar. Be sure to use an alcohol-free mouthwash, as alcohol can dry out your mouth and cause more bacteria to grow.
Antibiotic Therapy
If your periodontal disease is severe, your dentist may recommend a course of antibiotics to help control the infection. This may involve a topical antibiotic ointment or a systemic antibiotic taken orally.
Surgery
In severe cases, your dentist may recommend surgery. This may include flap surgeries, which involve lifting the gums to remove plaque and tartar and cleanse the infected area. It may also include bone or tissue grafts or the removal of excess gum tissue.
No matter how severe your periodontal disease is, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible. Your dentist can help you determine the best course of treatment for your specific case. With proper treatment, you can maintain good oral hygiene and prevent further damage to your teeth and gums.
Read More: Dental Implants, Tooth Extraction, Cosmetic Treatment, Dental Fillings
Prevention of Periodontal Disease
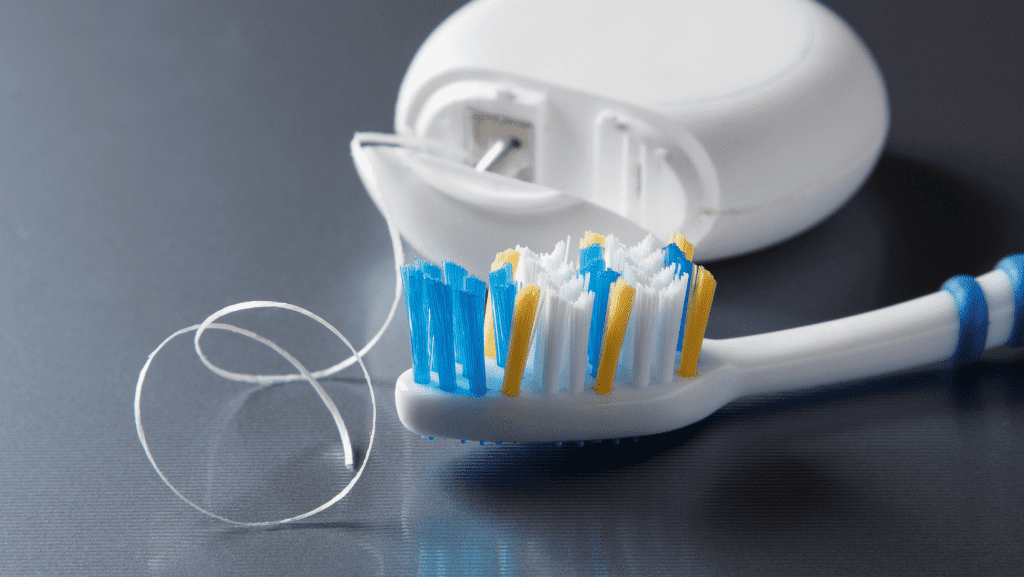

As a leading source of oral health, prevention of periodontal disease should be a top priority for everyone. There are steps that everyone can take to prevent periodontal disease and keep their teeth and gums healthy.
Brushing twice a day is key for preventing periodontal disease. Brushing helps to remove plaque from the surfaces of your teeth and along the gum line. Plaque is a sticky film that contains bacteria and when it is not removed, it can harden into tartar, which can lead to gum disease. Be sure to use a soft-bristled brush and to brush in circular motions to better remove plaque. Be sure to brush your tongue as well to remove bacteria that cause bad breath.
Flossing is just as important as brushing for preventing periodontal disease. Flossing helps to remove plaque and food particles that are stuck in between teeth and along the gum-line. For best results, use a waxed floss and floss gently in a sawing motion.
Visiting your dentist regularly is also important for preventing periodontal disease. During the check-up, your dentist will look for signs of periodontal disease such as red and swollen gums, receding gums, and bad breath. Your dentist can also provide a professional cleaning, which can help to remove plaque and tartar that has built up over time.
Finally, quitting smoking is essential for preventing periodontal disease. Smoking damages the gums and teeth, making them more susceptible to infection. Smoking also increases the risk of other serious health issues such as cancer and heart disease.
By following these steps, you can help to prevent periodontal disease and ensure that your teeth and gums stay healthy. Remember to brush twice a day, floss every day, visit your dentist regularly, and quit smoking. These steps can help you maintain a healthy smile for life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, periodontal disease is a serious condition that can have a major impact on your oral health. It is important to understand the causes of periodontal disease and to take steps to prevent it from happening in the first place.
Once periodontal disease does occur, it is important to seek treatment for it as soon as possible to avoid further damage to your teeth and gums. With proper preventative care and treatment, it is possible to keep periodontal disease from progressing to an even more serious stage.
Your teeth are an important part of your body and health. It’s crucial to maintain good dental hygiene at home and visit your dentist or periodontist frequently if you have signs of gum disease then gum disease cures first, if it is in the final stage of gum disease then consult your periodontist near me. You can maintain the health of your teeth and gums with the right care.
FAQs

How to treat Gum Disease?
Periodontal disease is typically treated with a variety of methods, including scaling and root planing, antimicrobial therapy, oral hygiene instructions, and in more advanced cases, surgery. Scaling and root planing involves the removal of plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line. Antimicrobial are used to reduce the bacterial population in the mouth, and oral hygiene instructions are given to help prevent the re-occurrence of periodontal disease. In more advanced cases, surgery may be needed to repair damaged tissue and bone or to remove infected gum tissue.
Can a regular dentist treat gum disease?
Similar to how an orthodontist can provide more specific braces alternatives than most general dentists, periodontists can provide more specialist care and attention even though general dentists are also certified to treat periodontal disease.
How much does it cost to clean gum disease?
Deep cleanings assist address gum disease by polishing the surface of the roots as well as the visible parts of the teeth. Without insurance, this procedure could cost between $150 and $300 and frequently last for several hours. However, this cost will vary because it is only an average.
When is a gum infection an emergency?
If the infection has grown so painful that it cannot be treated with over-the-counter medication, the patient should call for emergency assistance. If the patient is showing signs of having a tooth abscess, such as developing a fever, feeling chills, vomiting, or other symptoms.
How do you know if you have Periodontal Disease?
The best way to know if you have periodontal disease is to visit your dentist for an examination. During a periodontal exam, your dentist will look for signs of inflammation in the gums, bone loss, and loose teeth. Your dentist may also use special tools to measure the pockets around your teeth, which can indicate the severity of periodontal disease. If any signs of periodontal disease are found, your dentist will discuss treatment options with you.
What are the three stages of gum disease?
Stage 1 of periodontists: the initial. Stage two of periodontists: Moderate periodontists, Stage 3 of periodontists: Severe with a risk of tooth loss.
What happens if you leave gum disease untreated?
Gum disease is called periodontist (also known as periodontal disease). Your teeth’s soft tissue is harmed by an infection, and the bone that supports them is eroded. If the illness is not treated, the bone will eventually deteriorate, causing the teeth to become loose and eventually fall out.