Understanding the Nature of Laughing Gas
1. Brief History of Laughing Gas in Dentistry
This section of the blog would provide an overview of how laughing gas (or nitrous oxide, N₂O) has been used in the realm of dentistry, tracing its historical roots to its present-day applications.
Early uses and discoveries
This subsection would detail the initial instances of nitrous oxide’s recognition and utilization.
Sir Humphry Davy’s Experiments: The British chemist Sir Humphry Davy was one of the first people to document the effects of nitrous oxide. In the late 18th century, Davy conducted a series of experiments, inhaling the gas himself and noting its anesthetic and euphoric properties. He even suggested its potential use in surgical procedures to reduce pain, though his suggestion wasn’t immediately adopted.
“Painless operations”: As the 19th century progressed, nitrous oxide began to gain popularity as an anesthetic. Dr. Horace Wells, a dentist, after witnessing a nitrous oxide demonstration in 1844, recognized its potential in dentistry. He underwent the first known dental procedure using nitrous oxide as an anesthetic, marking a significant milestone in its dental application.
Nitrous Oxide Parties: Due to its euphoric effects, nitrous oxide became popular in recreational settings, known colloquially as “laughing gas parties.” These events, however, were quite distinct from their medical uses.
Evolution of its application in modern dentistry
This subsection would discuss the transition from the early, rudimentary uses of nitrous oxide to its refined, sophisticated, and widespread application in today’s dental procedures.
Introduction as a Sedative: The early 20th century saw more controlled and standardized use of nitrous oxide in dentistry. Dental professionals recognized its value not just as an anesthetic but also as a sedative, especially for patients who experienced dental anxiety.
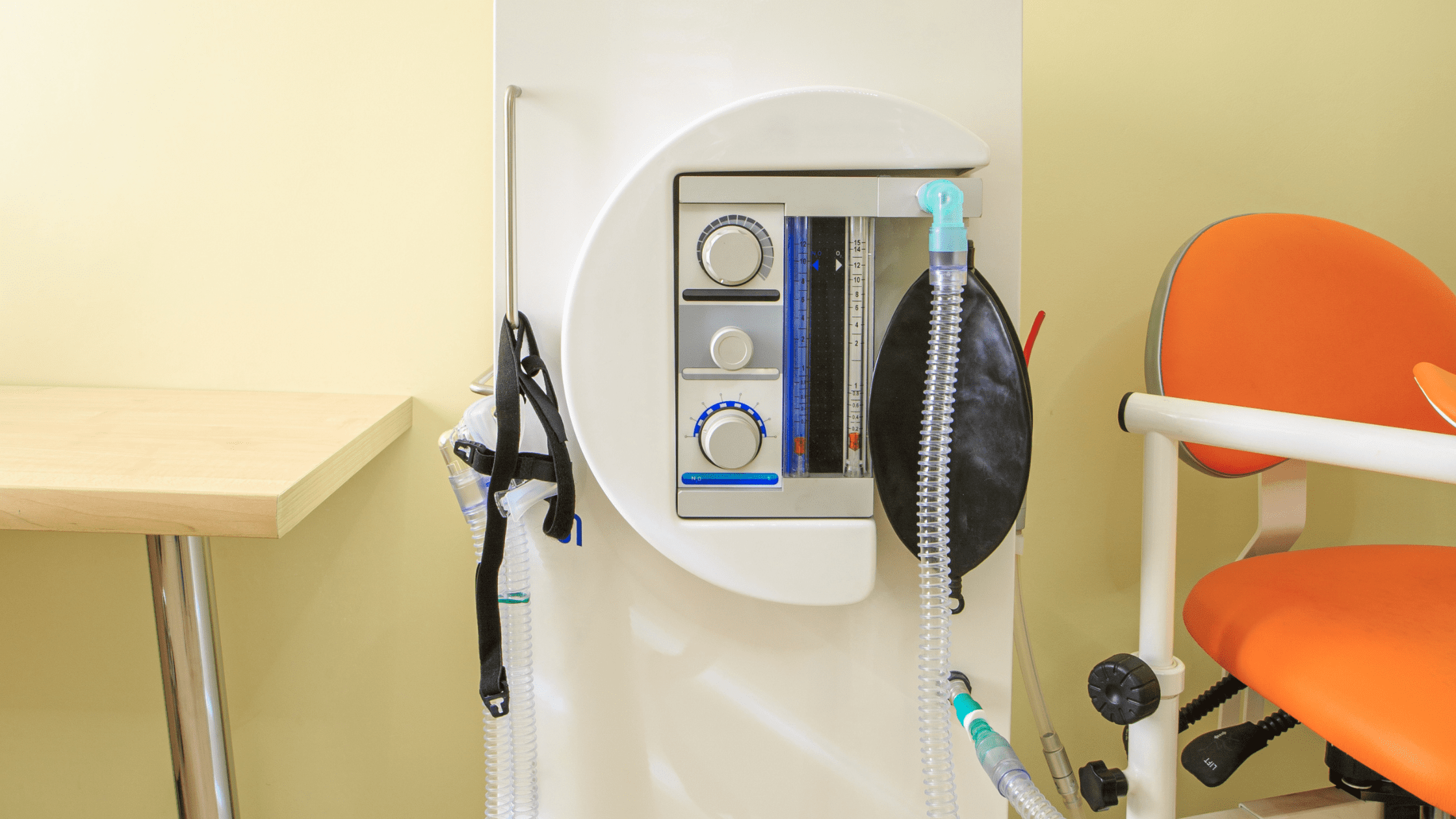
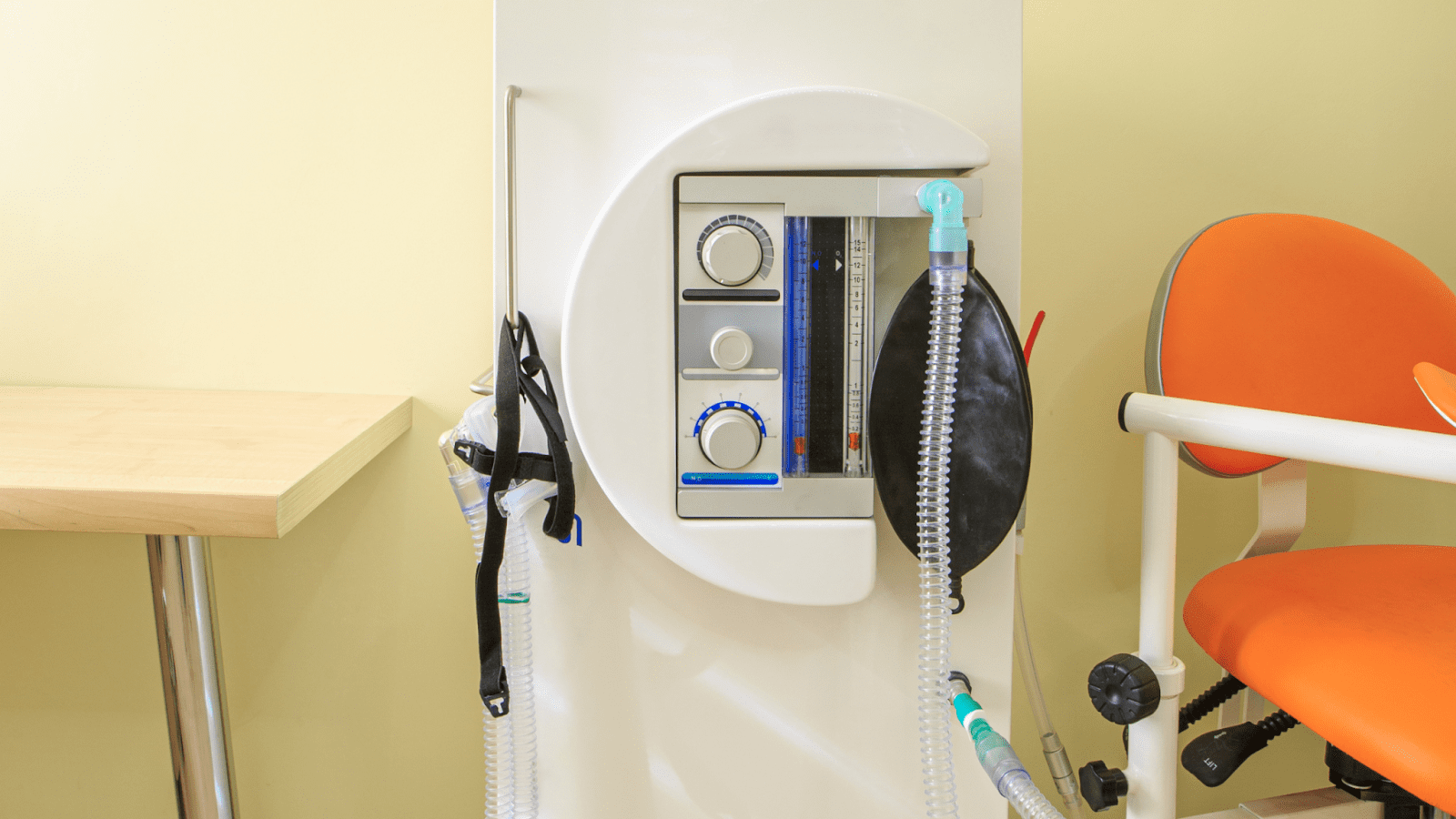
Advancements in Delivery Systems: As technology advanced, so did the apparatus used to administer nitrous oxide. Modern systems allow for a precise mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen, ensuring the patient receives a safe concentration. Additionally, nasal masks became more comfortable, further enhancing the patient’s experience.
Widespread Acceptance: Today, nitrous oxide sedation is a commonly accepted and widely used practice in dental offices worldwide. Its safety profile, combined with its effectiveness in calming anxious patients and providing pain relief, makes it a staple in many dental procedures.
2. What Exactly is Laughing Gas?
This section of the blog will delve into the specifics of what nitrous oxide, commonly referred to as “laughing gas,” is. It aims to provide readers with a clearer understanding of the substance from a chemical perspective and its physiological effects when inhaled by humans.
Composition and Properties
In this subsection, the basic nature of nitrous oxide will be described, shedding light on its unique properties that make it suitable for medical and dental applications.
Chemical Composition: Nitrous oxide (N₂O) is composed of two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It’s a colorless and non-flammable gas at room temperature, with a slightly sweet odor and taste.
Physical State: It is typically stored in compressed gas cylinders and turns into a liquid under high pressure. When released, it rapidly vaporizes back into its gaseous state.
Stability: Nitrous oxide is relatively stable but can break down at high temperatures to produce oxygen and nitrogen. This property has led to its use as an oxidizer in rocket propulsion.
Solubility: It’s moderately soluble in water and fats, which plays a role in its rapid uptake and elimination in the human body
Its Mode of Action on the Human Body
Here, the blog will discuss how nitrous oxide interacts with the body to produce its characteristic effects, including sedation, pain relief, and euphoria.
Inhalation: When inhaled, nitrous oxide is absorbed rapidly through the lungs into the bloodstream. From there, it travels to the central nervous system, where it exerts its primary effects.
Central Nervous System (CNS) Effects: Nitrous oxide has a depressant effect on the CNS. This results in pain relief, sedation, and a feeling of euphoria in many individuals. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it’s believed that N₂O affects the release of certain neurotransmitters, possibly inhibiting pain signals and amplifying inhibitory neurotransmission.
Rapid Elimination: One of the benefits of nitrous oxide is its fast elimination from the body. Once inhalation stops, the effects of the gas wear off quickly. This is because it’s not metabolized to a significant extent in the body and is exhaled unchanged, allowing for rapid recovery.
Safety Profile: When administered in controlled conditions, such as in a dental office with a proper mix of oxygen, nitrous oxide is considered safe. It doesn’t depress the respiratory system as profoundly as some other anesthetics can. However, if abused or used in a non-medical setting without adequate oxygen, it can lead to harmful effects, including hypoxia.
3. Primary Benefits in Dental Procedures
In dental procedures, the use of nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, offers several notable advantages that enhance both the patient’s experience and the dentist’s ability to perform procedures efficiently.
Immediate Calming Effect
Nitrous oxide is known to induce a sense of relaxation and even euphoria in patients. This is especially valuable in a dental setting where patients might experience anxiety or fear. The calming effect can make the dental experience more pleasant and less intimidating for the patient.
Rapid Onset and Offset
One of the standout features of laughing gas is how quickly it begins to work and how swiftly its effects wear off. Within minutes of inhaling the gas, patients feel its calming and pain-relieving properties. Similarly, once the gas is turned off and regular oxygen is administered, the effects diminish rapidly. This means patients can often drive themselves home post-procedure without lingering effects.
Control Over Depth of Sedation
Dentists can adjust the concentration of nitrous oxide being administered, giving them precise control over the depth of sedation. This ensures that the patient remains comfortable throughout the procedure, neither too sedated nor insufficiently relaxed. Furthermore, the patient remains conscious, allowing for communication with the dental professional, which can be crucial during certain procedures.
These benefits underscore why nitrous oxide is a favored choice in many dental practices, combining both patient comfort and procedure efficacy.
4. Comparing Laughing Gas to Other Sedation Methods
The use of sedation in medical and dental procedures varies based on the method employed. Let’s compare nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, to other prevalent sedation techniques, focusing on its advantages and safety profile.
Advantages over IV Sedation or General Anesthesia
Non-Invasive: Laughing gas is administered via a nasal mask, making it non-invasive compared to the needles required for IV sedation. This is particularly beneficial for patients with a fear of needles.
Conscious Sedation: While under the effects of nitrous oxide, patients remain conscious and can respond to instructions. In contrast, general anesthesia renders patients unconscious, and IV sedation often results in deeper sedation where patients might not remember the procedure.
Quick Recovery: Post-procedure recovery time for laughing gas is considerably shorter. Patients can often resume their normal activities or even drive themselves home shortly after, unlike after general anesthesia or IV sedation, which requires a longer observation period and often assistance getting home.
Immediate Onset: As mentioned earlier, nitrous oxide acts rapidly, allowing dental professionals to start the procedure shortly after administration. Some other sedation methods may have a longer onset time.
Safety Profile and Minimal Side Effects
Tried and Tested: Laughing gas has been used for over a century and has a proven track record of safety when administered properly.
Minimal Side Effects: While any sedative can have side effects, those associated with nitrous oxide (like nausea or dizziness) are typically mild and wear off quickly. In contrast, other sedation methods might come with a more extensive list of potential side effects or risks.
Doesn’t Depress Respiratory System Profoundly: Nitrous oxide, when administered with oxygen, usually doesn’t depress the respiratory system to the extent that some other sedatives might. This means that patients keep breathing regularly, which is inherently safer.
Controlled Depth: As stated previously, the dentist can control the depth of sedation with nitrous oxide, ensuring the patient doesn’t become overly sedated.
In summary, while all sedation methods have their place and benefits, laughing gas offers a unique combination of safety, convenience, and comfort, making it a preferred choice for many dental procedures.
Patient-Centric Benefits of Laughing Gas

When choosing sedation methods in dental practices, the patient’s comfort and well-being are paramount. Laughing gas, or nitrous oxide, offers several benefits that are directly aligned with patient concerns and convenience.
1. Addressing Dental Anxiety
How it Helps Alleviate Patient Fears:
Many individuals experience trepidation at the thought of dental procedures. Laughing gas acts swiftly to induce a relaxed, calm state, allowing patients to approach their treatments with less anxiety. The immediate calming effect helps to temper any fears and provides a more pleasant dental experience.
Increasing Comfort During Potentially Uncomfortable Procedures:
Beyond psychological comfort, laughing gas also provides physical comfort. For procedures that may induce discomfort, the analgesic (pain-relieving) properties of nitrous oxide ensure that patients remain at ease.
2. No Extended Recovery Needed
Quick Dissipation from the System:
One of the standout features of laughing gas is its rapid onset and offset. Once the administration stops, nitrous oxide is quickly eliminated from the body, allowing patients to feel normal in a short span.
Patients Can Often Drive Themselves Post-Procedure:
Given its rapid offset, and unlike other deeper sedation methods, patients are usually able to drive themselves home after the procedure. This offers a significant convenience factor, eliminating the need for an accompanying person.
3. Minimal Side Effects and Maximum Comfort
Reduced Risk Compared to Other Sedation Methods:
Nitrous oxide has a well-established safety profile. When compared to other sedation methods, like IV sedation or general anesthesia, the risks associated with laughing gas are considerably lower.
No Lingering Grogginess or Hangover:
Some sedation methods may leave patients feeling groggy, disoriented, or even nauseated post-procedure. With laughing gas, these after-effects are typically minimal or non-existent, allowing patients to resume their daily activities without any “hangover.”
4. Flexible Use Across Different Procedures
From Cleanings to Extractions:
The versatility of nitrous oxide is noteworthy. It can be used in a variety of dental procedures, ranging from simple cleanings where the patient might just be anxious, to more involved processes like tooth extractions.
Ideal for Both Adults and Children:
Laughing gas isn’t just for adults. Its mild and controllable nature makes it suitable for pediatric dentistry as well. Children, who might be particularly apprehensive about dental visits, can benefit from the calming effects of nitrous oxide.
In conclusion, the patient-centric benefits of laughing gas make it an exceptional choice in dental care. It aligns with the principles of ensuring patients’ comfort, safety, and convenience, making dental procedures a more manageable experience for all.
Addressing Concerns and Highlighting Advantages
Navigating the world of dental sedation can be a complex endeavor for many. With varied options available, understanding the pros and cons of each becomes crucial. In this outline, we will address some prevalent concerns regarding laughing gas, or nitrous oxide, and emphasize its advantages.
1. Debunking Myths About Laughing Gas
Addressing Common Misconceptions:
Many people mistakenly believe that nitrous oxide can make them unconscious or that it’s similar to recreational drug use. Addressing such misconceptions by presenting factual information will be essential to ensure patients are well-informed.
Clarifying its Safety and Usage:
Contrary to some beliefs, when used in medical settings with proper administration, laughing gas is very safe. Highlighting its long history in dentistry and the stringent guidelines for its use can help cement its reputation as a trustworthy sedation option.
2. The Environmental and Operational Safety of Nitrous Oxide
Storage, Administration, and Disposal:
The handling of nitrous oxide in a dental setting is governed by specific guidelines to ensure both patient and environmental safety. Discussing its non-flammable nature, storage in compressed gas cylinders, and safe disposal methods reinforces its operational safety.
Low Environmental Impact:
Unlike some other gases, nitrous oxide has a minimal environmental footprint when used in medical contexts. It’s essential to differentiate between its controlled medical use and other industrial uses that might contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Affordability and Cost-Efficiency
Cost Comparisons with Other Sedation Methods:
When compared to more intensive sedation methods, like IV sedation or general anesthesia, laughing gas can often be a more cost-effective choice. It doesn’t require extensive monitoring equipment or specialized anesthetists, which can drive up costs.
Insurance Coverage and Patient Affordability:
Most dental insurance plans recognize the benefits and safety of nitrous oxide, and it’s often covered, at least in part, under many policies. This can make it a more accessible option for many patients.
4. Case Studies and Testimonials
Real-World Examples of Successful Use:
Providing actual case studies where laughing gas was employed can serve as a powerful testament to its efficacy. Whether it’s a nervous first-time patient or a complex dental surgery, real-world examples paint a vivid picture of its advantages.
Patient Stories of Positive Experiences with Laughing Gas:
There’s nothing more reassuring than hearing from someone who’s been through it. Sharing patient testimonials, their initial apprehensions, and eventual positive experiences can instill confidence in those considering nitrous oxide as a sedation option.
In sum, when it comes to laughing gas, understanding is the antidote to apprehension. By debunking myths, and underscoring its safety, affordability, and real-world efficiency, we can paint a comprehensive and reassuring picture for those considering this form of dental sedation.