At My Gentle Dentist, we prioritize your oral health and strive to provide comprehensive care to ensure your smile lasts a lifetime. Gingivitis is a common yet reversible gum disease that, if detected early, can be treated effectively. Left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. In this blog, we will delve into the symptoms of gingivitis, how to identify them, and what steps you can take to address them.
1. Red or Swollen Gums
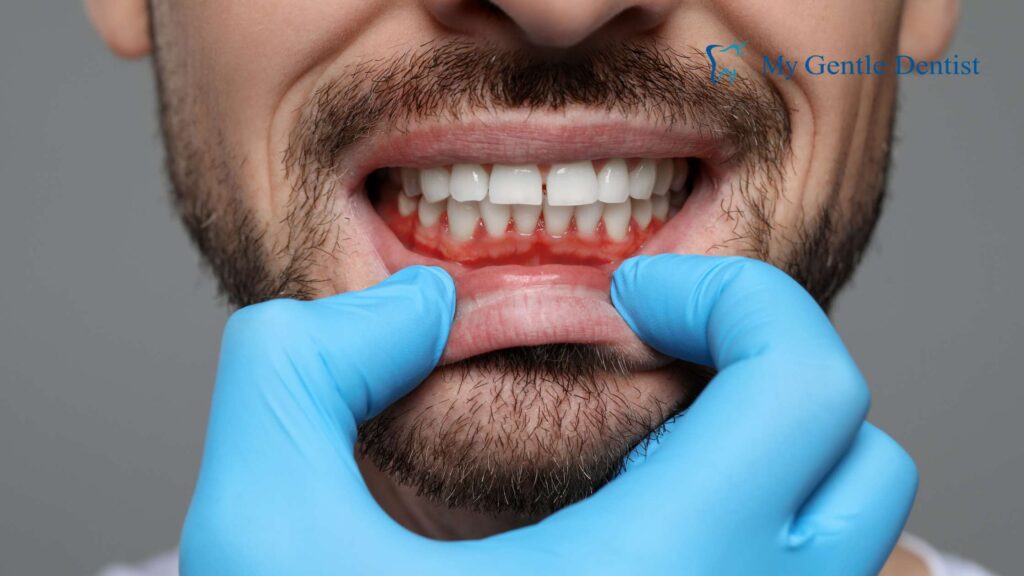
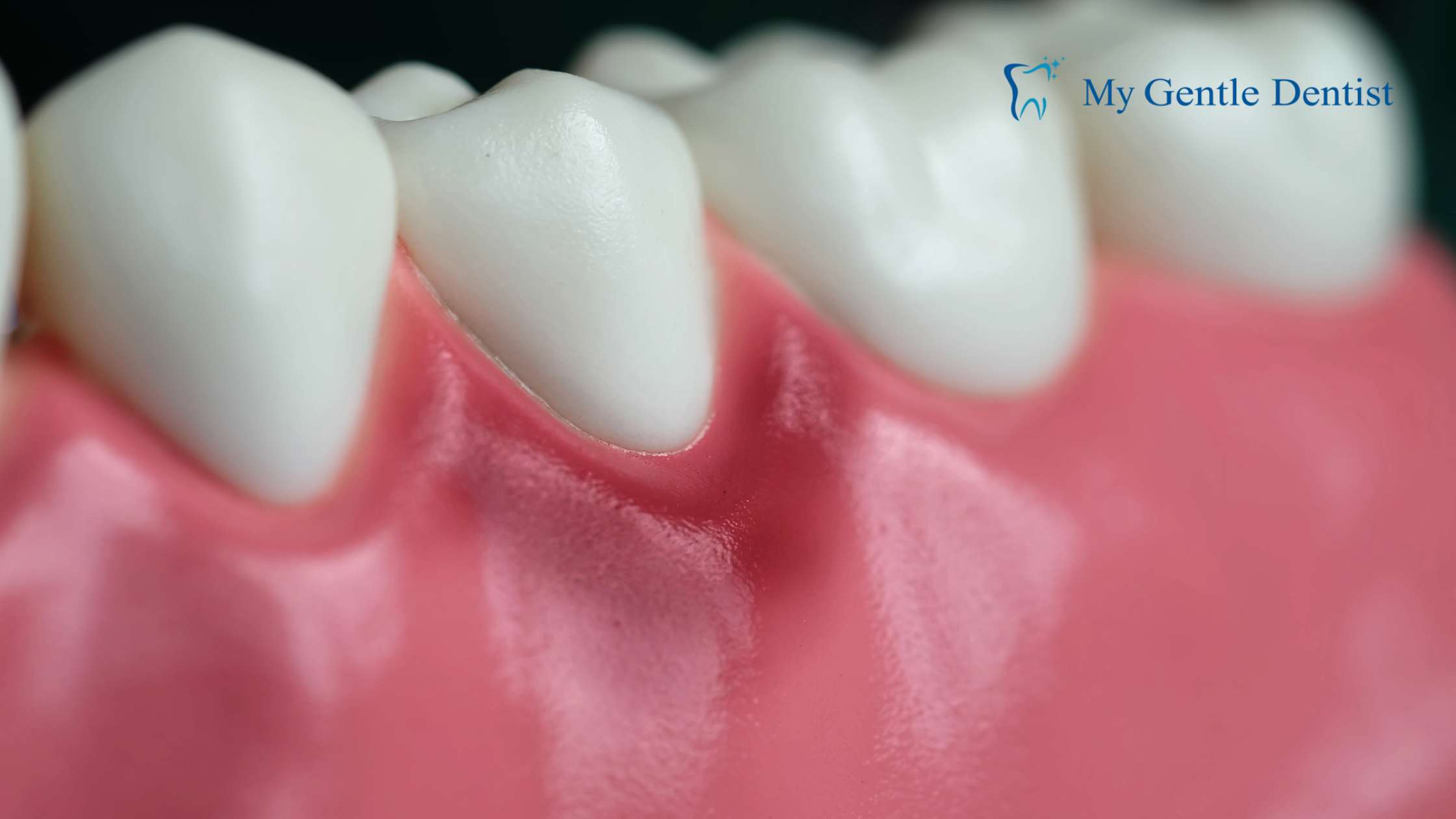
Healthy gums are firm and pink. However, one of the first symptoms of gingivitis is red, swollen gums that feel tender when touched. This inflammation is caused by plaque buildup, which contains harmful bacteria that irritate the gums.
How to Address It:
- Brush your teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss once a day to remove plaque buildup between teeth.
- Use an anti-bacterial mouthwash to reduce bacterial growth.
- Schedule a professional cleaning with your dentist to remove plaque and tartar.
Early intervention is crucial. If you notice persistent redness or swelling, don’t delay seeking care. Book an appointment today with My Gentle Dentist.
2. Bleeding Gums During Brushing or Flossing
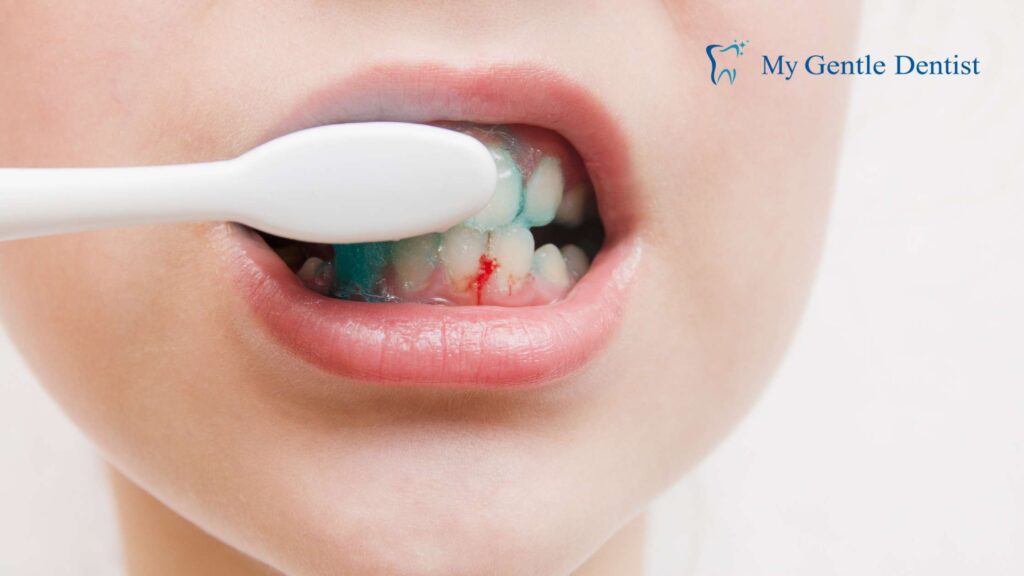
If your gums bleed easily while brushing or flossing, it’s a common indication of gingivitis. Bleeding occurs because the bacteria in plaque irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation.
Preventive Measures:
- Switch to a gentle brushing technique to avoid further irritation.
- Floss gently and regularly to remove food particles and plaque.
- Avoid tobacco products, which can worsen gum health.
- See your dentist for a professional cleaning.
Ignoring bleeding gums can lead to more severe conditions like periodontitis. Learn about our gum disease treatments here.
3. Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
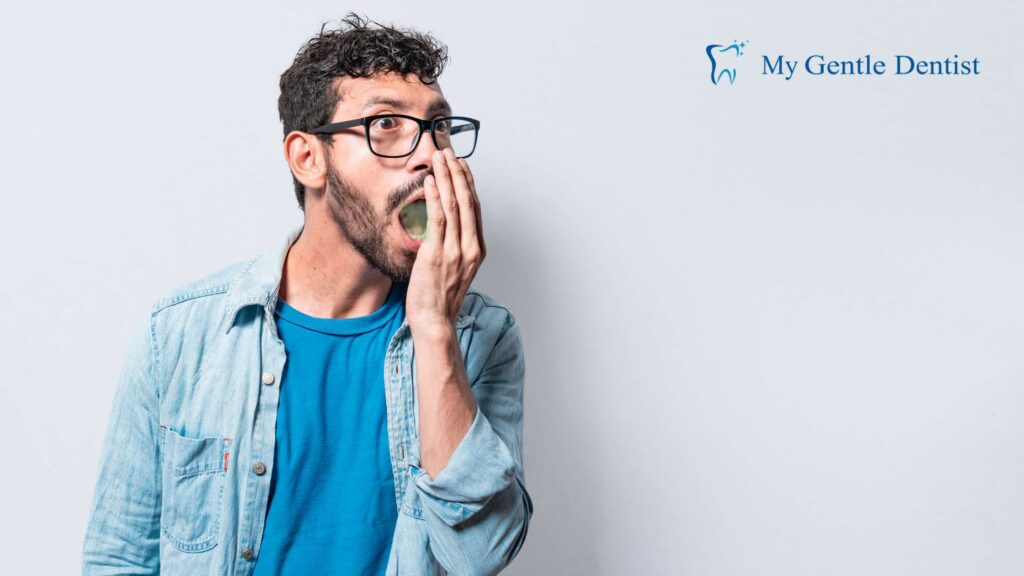

Chronic bad breath, or halitosis, is more than an inconvenience; it is often a sign of poor oral health. The bacteria in plaque produce unpleasant-smelling compounds as they break down food particles.
Key Causes of Halitosis:
- Plaque and tartar accumulation.
- Dry mouth reducing saliva production.
- Gum infections causing bacterial overgrowth.
How to Address It:
- Brush your tongue along with your teeth to remove bacteria.
- Stay hydrated and chew sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production.
- Use mouthwash specifically designed to combat bad breath.
- Seek professional treatment for gingivitis if bad breath persists.
| Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
| Plaque accumulation | Regular brushing and flossing |
| Dry mouth | Drink water and use oral rinses |
| Advanced gum infection | Professional dental care |
4. Tender or Painful Gums
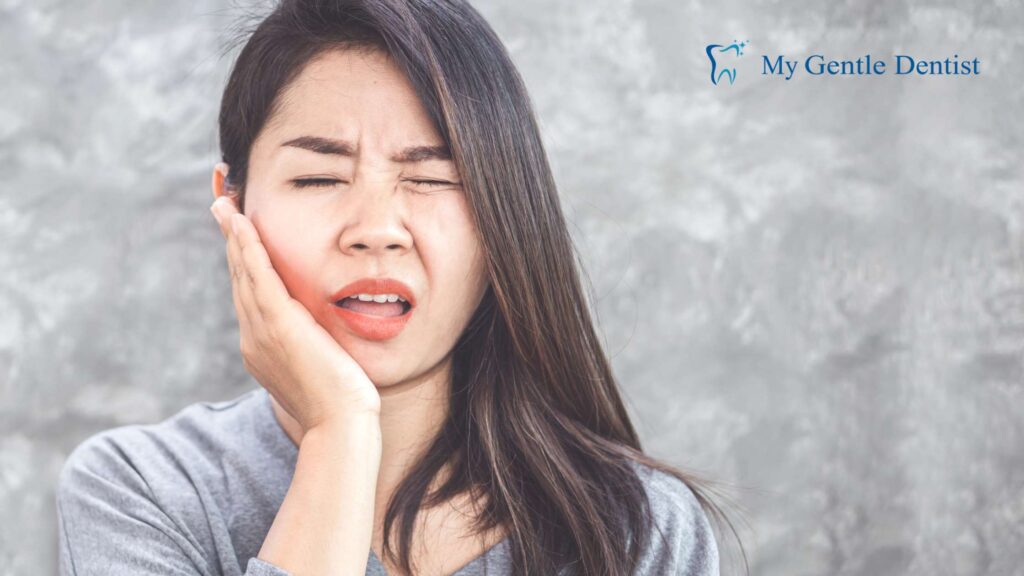

Tender or painful gums can make everyday activities like eating or brushing uncomfortable. This symptom often points to an advanced stage of gingivitis where the inflammation has intensified.
Treatment for Tender Gums:
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water to reduce inflammation.
- Apply a cold compress to the affected area to alleviate pain.
- Use over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications if necessary.
- Schedule an examination with your dentist to determine the underlying cause.
Persistent gum pain could indicate more severe issues. Don’t wait—contact us today for expert care.
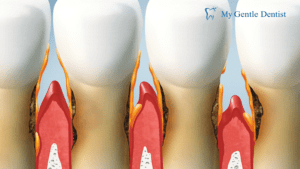
5. Receding Gums
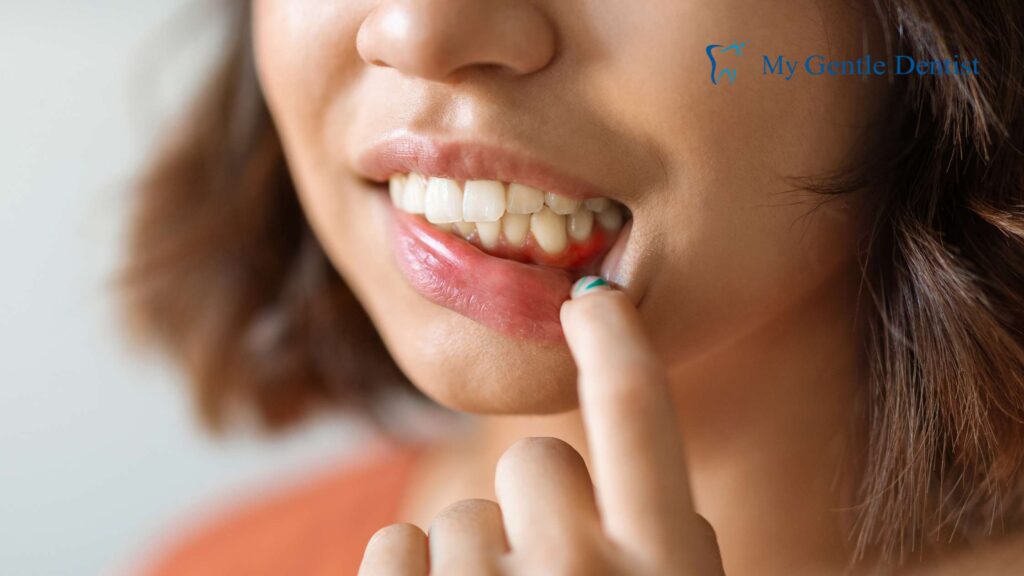

Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue pulls back from the tooth, exposing the roots. This is not only unsightly but also increases the risk of tooth decay and sensitivity.
How Gingivitis is Treated in Such Cases:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep-cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar below the gumline.
- Gum Grafting: In advanced cases, gum grafting can restore the gumline.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly can prevent further gum recession.
Long-Term Effects of Receding Gums:
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
- Higher risk of root decay.
- Changes in the appearance of your smile.
6. Loose Teeth

Gingivitis weakens the connection between your teeth and gums. If untreated, the supporting structures of your teeth, such as the jawbone, may also deteriorate, causing teeth to loosen or shift.
How to Address Loose Teeth:
- Undergo a professional evaluation to determine the extent of the damage.
- Opt for a deep cleaning or surgical intervention, such as flap surgery or bone grafting.
- Consider tooth replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges, if teeth cannot be saved.
At My Gentle Dentist, we provide personalized treatment plans to address advanced gum disease. Learn more about our services here.
7. Gum Discoloration
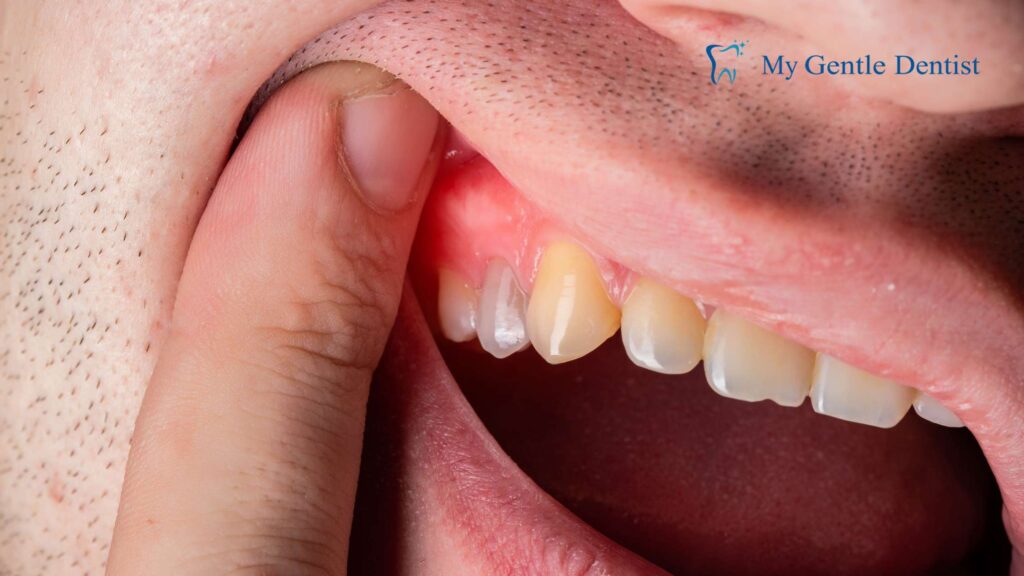
Discoloration of the gums, such as dark red, purple, or grayish tones, is often a sign of decreased oxygen supply due to severe inflammation. This can be accompanied by other symptoms like swelling or tenderness.
Treatment Options:
- Professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar.
- Antibiotics to control infection in severe cases.
- Consistent oral hygiene practices to prevent recurrence.
8. Pus Between Teeth and Gums
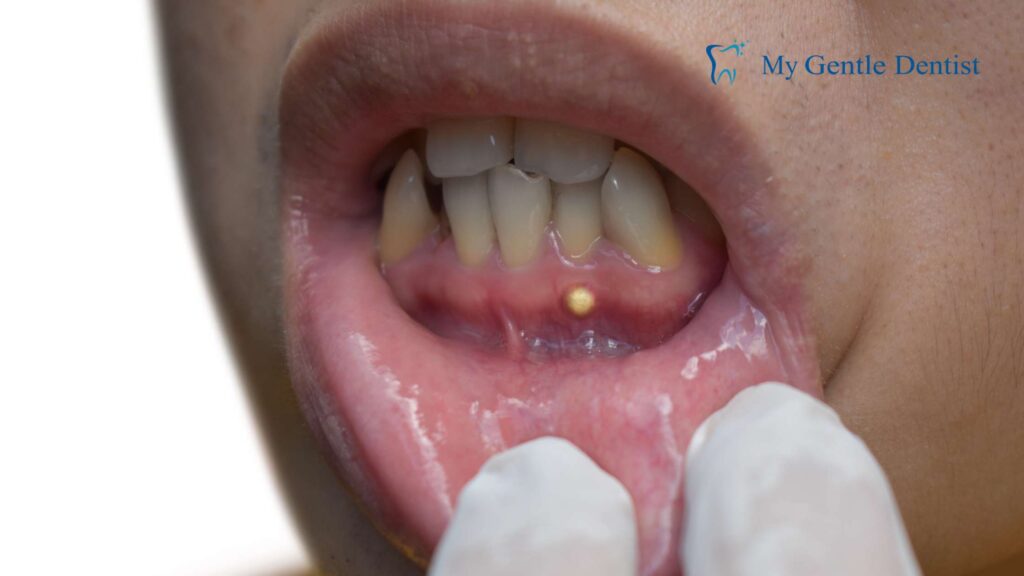
The presence of pus, or gum abscesses, indicates a severe infection requiring immediate dental intervention. This symptom typically signals the transition from gingivitis to periodontitis.
Treatment for Gum Abscesses:
- Drain the abscess to relieve pain and remove infection.
- Administer antibiotics to control bacterial growth.
- Perform scaling and root planing to clean the affected areas.
9. Increased Tooth Sensitivity
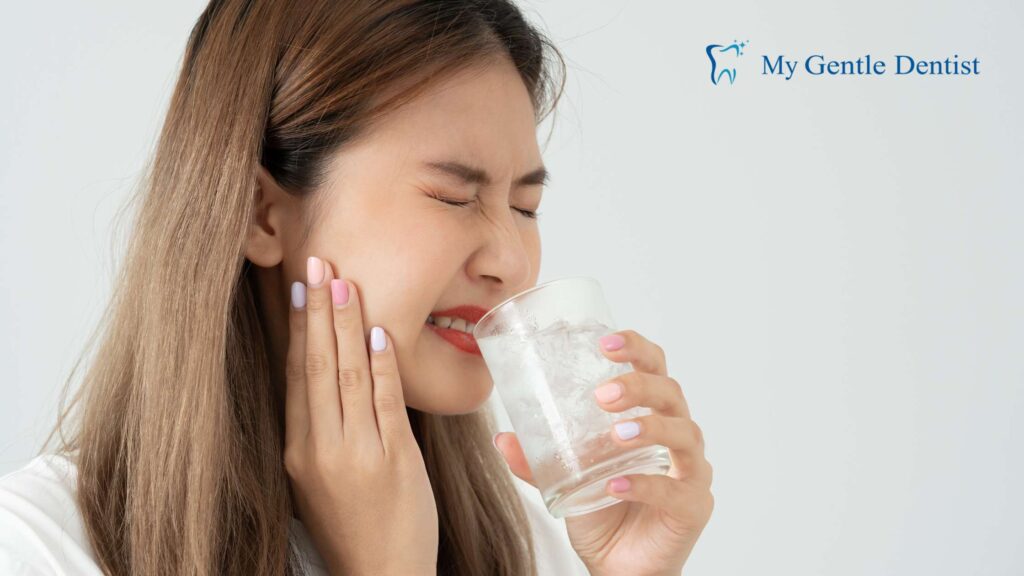

Sensitivity to hot or cold food and beverages often occurs when the roots of your teeth are exposed due to gum recession or enamel erosion. This can make eating and drinking uncomfortable.
Ways to Manage Sensitivity:
- Use toothpaste specifically designed for sensitive teeth.
- Avoid acidic foods and drinks that can erode enamel.
- Consult your dentist about applying fluoride treatments or dental sealants.
10. Changes in Bite Alignment
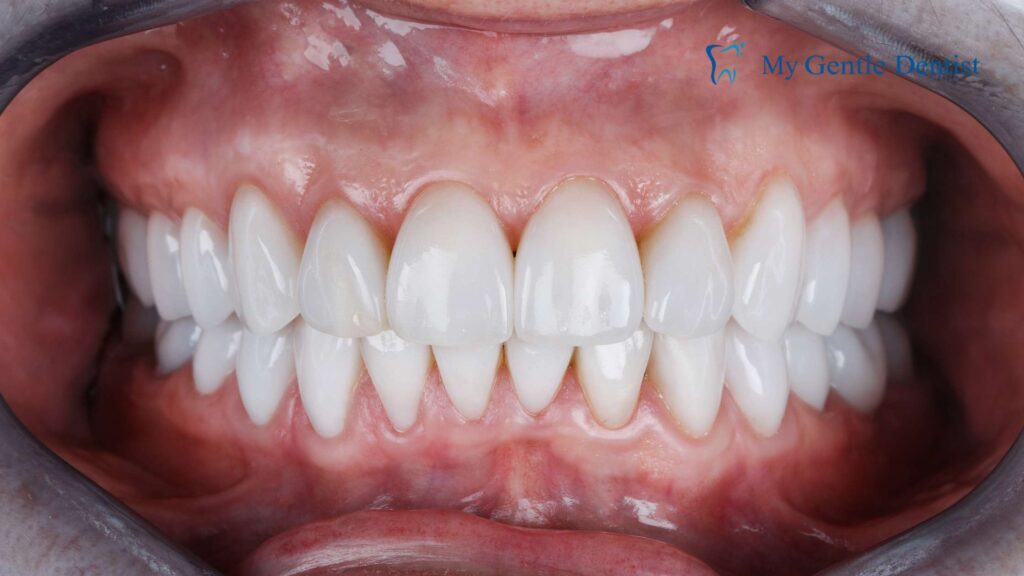
Gingivitis weakens the gums and supporting structures, which can cause teeth to shift slightly. Over time, this may alter the way your upper and lower teeth fit together when you bite down.
Corrective Measures:
- Orthodontic treatments like braces or aligners to restore proper alignment.
- Occlusal adjustments to reshape the biting surfaces of the teeth.
- Regular dental monitoring to prevent further misalignment.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a dental professional. Early detection and treatment of gingivitis can save your gums and teeth from irreversible damage.
Why Choose My Gentle Dentist?
- Comprehensive gum disease treatments tailored to your needs.
- State-of-the-art dental technology for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- A compassionate team dedicated to improving your oral health.
Don’t wait until gingivitis progresses. Book your appointment today!
Conclusion: Protect Your Oral Health
Recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis early and taking immediate action is the key to maintaining healthy gums. Whether it’s a professional cleaning, advice on treatment for gingivitis, or tips on how gingivitis is treated, we’re here to help you at every step.
Visit My Gentle Dentist for expert care and personalized treatment. Schedule your appointment today!
Gingivitis Symptoms and Solutions
| Symptom | Solution |
|---|---|
| Red or swollen gums | Gentle brushing, flossing, and professional cleaning |
| Bleeding gums | Flossing regularly, anti-inflammatory mouthwash |
| Persistent bad breath | Tongue brushing, mouthwash, dental check-ups |
| Gum discoloration | Professional cleaning, antibiotics |
| Loose teeth | Scaling and root planing, surgical interventions |
For more information, explore our dedicated page on gum disease treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the common symptoms of gingivitis?
Common symptoms of gingivitis include swollen gums, redness around the gum line, bleeding during brushing or flossing, bad breath, receding gums, and tenderness in the gums. These signs of gingivitis indicate inflammation of the gums and should be addressed promptly.
How is gingivitis diagnosed by a dentist or dental hygienist?
Gingivitis is diagnosed through a dental examination where the dentist or dental hygienist will check for signs of gum disease, including probing around the teeth to measure gum pocket depth and examining the condition of the gums for redness or swelling.
What causes gingivitis?
The primary cause of gingivitis is the buildup of plaque along the gum line. Poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, certain medical conditions, and hormonal changes can also increase the risk of developing gingivitis.
How can I treat gingivitis effectively?
To treat gingivitis, it is essential to improve oral hygiene by brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings. Professional dental treatments may also be necessary to remove tartar and address any underlying issues.
Can gingivitis lead to more serious gum disease?
Yes, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more advanced stage of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and damage to the bone supporting the teeth.
How can I prevent gum disease and gingivitis?
To prevent gum disease and gingivitis, maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly, use an antibacterial mouthwash, avoid tobacco products, and schedule regular check-ups with your dentist or dental hygienist.
What are the warning signs of gingivitis I should look for?
Warning signs of gingivitis include persistent bad breath, bleeding gums when brushing or flossing, swollen or tender gums, and changes in gum color. Recognizing these signs early is key to preventing progression to more severe gum disease.
How can I address the symptoms of gum disease at home?
To address symptoms of gum disease at home, practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing daily, use a soft-bristled toothbrush, and consider using a toothpaste designed to help treat gum issues. However, it is crucial to consult your dentist for a proper evaluation.
What is the relationship between gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gingivitis is an early form of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums, while periodontitis is a more severe stage of gum disease that can lead to loss of tissue and bone. If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis.